Stepper motors are widely used for their precise stopping capability and ease of use. They allow control of both the amount of rotation and speed using a simple digital square wave pulse signal. Unlike servo motors, they do not require an encoder to function. Examples of applications include CNC machines, index tables, robotics, scanners, and more recently, 3D printers.
There are various types of stepper motors available in the market. The most popular is the hybrid type, which combines features from permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors. Hybrid motors come in 2-phase, 5-phase, and high-resolution designs. They can also be pre-assembled with additional options such as electromagnetic brakes, encoders, or gearheads.
Choosing the right type of stepper motor depends on your application. Here are some scenarios where specific types might be preferred:
|
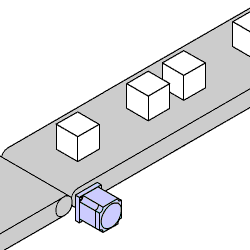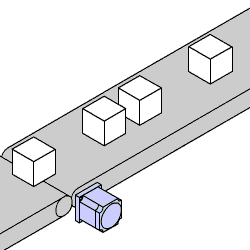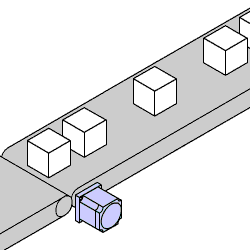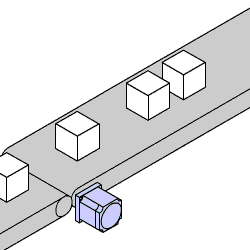
| Application: Performing quick indexing operations over short distances |
| Recommended: High torque 2-phase stepper motors |
High torque 2-phase stepper motors are commonly used and found in devices like ATM machines and slot machines. They offer high torque at low speeds and are ideal for general position control. NEMA frame sizes range from 8 to 34 (20 mm to 90 mm), with torque ranging from approximately 2.8 oz-in to 22,255 oz-in depending on stack length. These motors typically have 4, 6, or 8 lead wires for bipolar and unipolar drivers.
In linear motion applications, they are often combined with external mechanisms like pulleys and belts for indexing conveyors or ball screws for linear actuators. While traditionally used for low-speed applications, more designs are now adopting bipolar-parallel winding type motors for better high-speed performance.
|
PKP Series 2-Phase Stepper Motor
|
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '251701bf-65bc-4497-9e2f-2ebfc11ca710', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '251701bf-65bc-4497-9e2f-2ebfc11ca710', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); Â |
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'a6ac64af-a949-494e-8b3f-0ab30027f749', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'a6ac64af-a949-494e-8b3f-0ab30027f749', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); |
Â
| Application: Achieving a high-speed reciprocating motion with less vibration |
| Recommended: High torque 5-phase stepper motors |
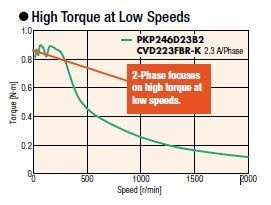
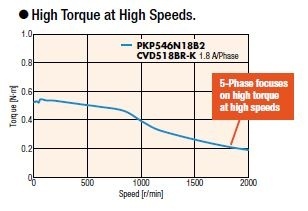
High torque 5-phase stepper motors with improved high-speed winding design are suitable for applications requiring fast reciprocating motions. Vibration is significantly lower than 2-phase motors even without microstepping. These motors have a step resolution of 0.72° instead of the typical 1.8°, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments like laboratory instruments.
|
PKP Series 5-Phase Stepper Motor
|
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'dfe6ec93-1e53-49d0-b7ac-808abc4f8ed4', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, 'dfe6ec93-1e53-49d0-b7ac-808abc4f8ed4', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); |
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '578af860-aea6-4f8b-b760-a8cfb2763d01', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '578af860-aea6-4f8b-b760-a8cfb2763d01', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"}); |
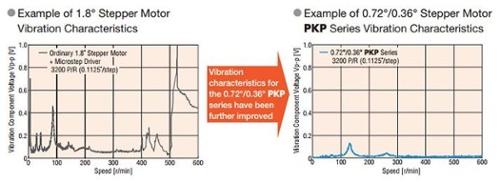
Since the basic step angle is small at 0.72° (0.36° for high-resolution type), the vibration and noise are considerably lower than 2-phase stepper motors with a basic step angle of 1.8°.
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '5123a609-ae54-4397-a1d1-e21e626c82c5', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '5123a609-ae54-4397-a1d1-e21e626c82c5', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Â
| Application: Performing indexing operations of large inertial loads |
| Recommended: Geared stepper motors |
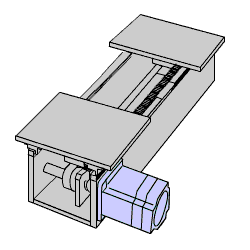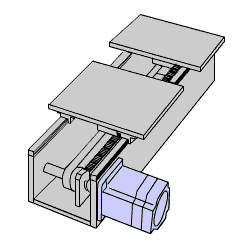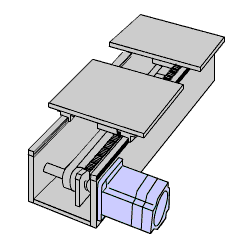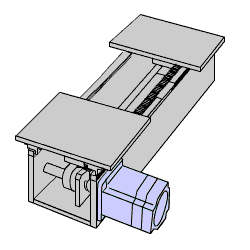
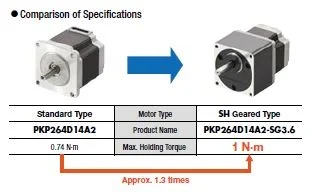
Geared stepper motors can rotate a larger inertial load, such as a robotic arm, due to their ability to generate much higher torque than round-shaft, ungeared motors, and to reduce the inertia ratio between the load and the motor. If the motor is not sized properly, large inertial loads can exceed the motor's recommended inertia ratio and cause missed steps due to overshooting or undershooting. Using a geared type stepper motor also increases the motor's ability to handle axial and radial loads.
 |
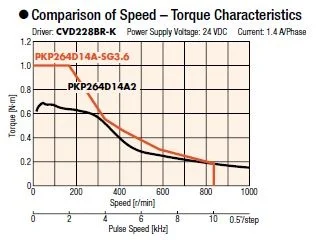 |
The new CS type centered shaft spur geared stepper motors offer improved torque, axial load, radial load, and backlash characteristics compared to traditional SH type offset shaft spur geared stepper motors. For users who prefer a centered shaft, the CS type provides a low-cost alternative to planetary gearheads. For users who need more torque or accuracy, planetary and harmonic geared motors are also available.
|
PKP Series CS Geared Type Stepper Motor |
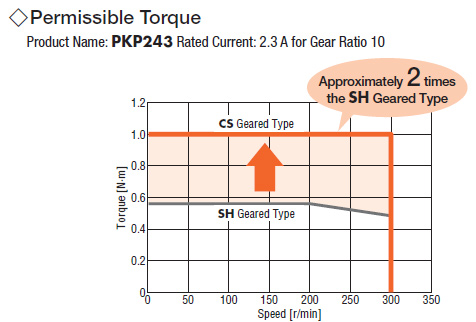 |
For space-saving machine designs, a geared type motor can drive heavier loads while keeping the motor frame size compact.
Â
| Application: Performing indexing operations with higher stop accuracy |
| Recommended: High resolution type 2-phase stepper motors |
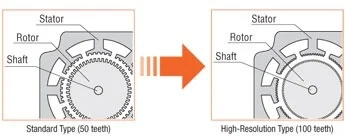
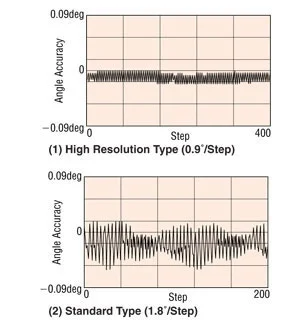
High resolution type 2-phase stepper motors have 100 rotor teeth instead of 50, doubling the basic step resolution from 200 to 400 steps per revolution and offering better stop accuracy (2 arc min or 0.034° instead of 3 arc min or 0.05°). Similar to 5-phase motors, these can "half-step" without a microstepping driver, which can lower costs for certain applications.
|
PKP Series High Resolution Type Stepper Motor
|
 |
 hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '27b3ac11-be8d-4f11-84d2-e784d759257e', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(2284573, '27b3ac11-be8d-4f11-84d2-e784d759257e', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Â
| Application: Performing vertical positioning operation with power-off braking |
| Recommended: Electromagnetic brake type stepper motors |
Electromagnetic brake type stepper motors are designed with a built-in power-off-activated electromagnetic brake that uses electromagnets and disc friction to hold the motor shaft in place. When power is removed or accidentally cut off, the electromagnetic brake can hold a load in position to prevent it from dropping or moving, such as in a rack and pinion lift. With an electromagnetic brake, the motor current can also be turned off at standstill to suppress heat or lower power consumption.
The electromagnetic brake is assembled at the rear of the motor, which increases the motor length.
|
PKP Series Electromagnetic Brake Type Stepper Motor
|
Tealight Candle Wax tealight candle
Material:Paraffin wax ,Soy Wax, Coconut Wax
Weight:8g to 23g
Package:50pcs/bag,100pcs/bag
Burning time:0.5hrs-8hrs
Color:white, red, blue, yellow, green etc
  Tealight candle,Tea light candle,Wax tealight candle,Paraffin wax tealight,cheap price white tealight candle Meichen(Hebei) Technology.,Ltd , https://www.mchenhome.com |